PREVALENCE AND ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE AMONG ADOLESCENTS IN RURAL COMMUNITIES, CENTRAL THAILAND: A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55374/jseamed.v3i2.49Keywords:
Substance abuse, adolescents, rural community, ThailandAbstract
Background: Substance abuse is one serious social challenge that has continued to in crease over a long time. This major problem currently affects society, the economy and national development. One related study conducted in southern Thailand found that the prevalence of substance abuse in youth groups was 7% in 2002 increasing to 9% and 13% in 2003 and 2004, respectively. Nevertheless, information regrading substance abuse among adolescents in Thailand remains limited especially in remote rural communities. The study aimed to determine the prevalence and associated factors concerning substance abuse.
Methods: The percent study was conducted in 2 high schools in rural communities, Chachoengsao and Sa Kaeo Provinces, central Thailand. A cross-sectional quantitative study identified the prevalence and associated factors of substance abuse among adolescents, A standardized self-reported questionnaire was used to collect data including demographic characteristics, history of substance abuse and associated factors. Multivariate analysis was performed to adjust confounders using logistic regression analysis.
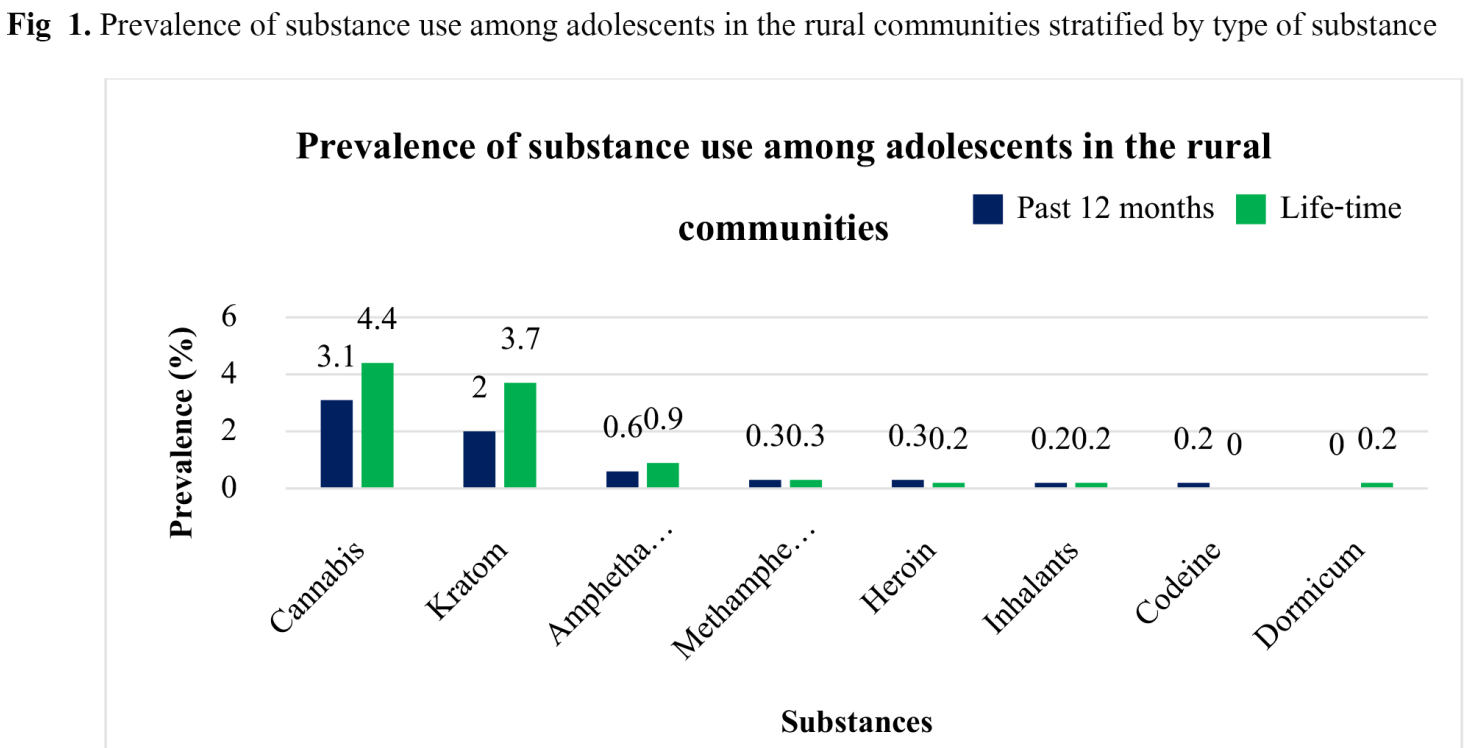
Results: The sample size of the study totaled 652 adolescents. The lifetime prevalence of substance abuse was 24.4% while the one-year prevalence of substance abuse was 16.7%. After adjusting for potential confounders, the risk factors associated with one year substance abuse among adolescents were being male (AORs; 2.19, 95%CI; 1.16-4.116), friend inducement (AORs; 3.28, 95%CI; 1.64-6.55), smoking (AORs; 3.22, 95%CI; 1.50-6.90) and alcohol consumption (AORs; 4.46, 95%CI; 2.43-8.16).
Conclusion: Our data emphasized that substance abuse was a problem in these rural communities, Public health interventions aimed to prevent substance abuse among adolescents should be designed and provided for these rural communities. Further, schools should provide lessons how to negotiate and avoid coercion when being induced to abuse substances or other unhealthy and dangerous behaviors.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Patrick ME, Wightman P, Schoeni RF, Schulenberg JE. Socioeconomic status and substance use among young adults: a comparison across constructs and drugs. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2012;73:772-82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2012.73.772
Daley DC. Family and social aspects of substance use disorders and treatment. J Food Drug Anal. 2013;21:S73-S6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2013.09.038
Pengpid S, Peltzer K. Prevalence and psychosocial correlates of illicit drug use among school-going adolescents in Thailand. Journal of Social Sciences. 2013;34:269-75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09718923.2013.11893138
Lander L, Howsare J, Byrne M. The impact of substance use disorders on families and children: from theory to practice. Soc Work Public Health. 2013;28:194-205. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19371918.2013.759005
DiMiceli LE, Sherman SG, Aramrattana A, Sirirojn B, Celentano DD. Methamphetamine use is associated with high levels of depressive symptoms in adolescents and young adults in Rural Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. BMC public health. 2016;16:168. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-2851-1
Center for Substance Abuse T. SAMHSA/CSAT Treatment Improvement Protocols. Substance Abuse Treatment for Persons With Co-Occurring Disorders. Rockville (MD): Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US); 2005.
Assanangkornchai S, Pattanasattayawong U, Samangsri N, Mukthong A. Substance use among high-school students in Southern Thailand: trends over 3 years (2002–2004). Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2007;86:167-74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.06.001
Desa U. World urbanization prospects, the 2011 revision. Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations Secretariat. 2014.
Hammond CJ, Mayes LC, Potenza MN. Neurobiology of adolescent substance use and addictive behaviors: treatment implications. Adolesc Med State Art Rev. 2014;25:15-32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1542/9781581108903-neurobiology
Angkurawaranon C, Jiraporncharoen W, Likhitsathian S, Thaikla K, Kanato M, Perngparn U, et al. Trends in the use of illicit substances in Thailand: Results from national household surveys. Drug and alcohol review. 2018;37:658-63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/dar.12689
Chomsri P, Aramrattana A, Siviroj P, Likhitsathian S. Substance use among students in Thailand. Journal of Ethnicity in Substance Abuse. 2018:1-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15332640.2018.1429974
Conger RD. The special nature of rural America. Rural substance abuse: State of knowledge and issues. 1997:37-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/e495612006-004
DeVoe JE, Krois L, Stenger R. Do children in rural areas still have different access to health care? Results from a statewide survey of Oregon's food stamp population. The Journal of Rural Health. 2009;25:1-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-0361.2009.00192.x
Siviroj P, Peltzer K, Pengpid S. Prevalence and psychosocial correlates of illicit drug use among school-going adolescents in Thailand. International Journal of Psychology. 2012;47:163-4.
Adkins JE, Boyer EW, McCurdy CR. Mitragyna speciosa, a psychoactive tree from Southeast Asia with opioid activity. Current topics in medicinal chemistry. 2011;11:1165-75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/156802611795371305
Assanangkornchai S, Muekthong A, Sam-Angsri N, Pattanasattayawong U. The use of Mitragynine speciosa (“Krathom”), an addictive plant, in Thailand. Substance use & misuse. 2007;42:2145-57. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10826080701205869
Becker JB, McClellan ML, Reed BG. Sex differences, gender and addiction. Journal of neuroscience research. 2017;95:136-47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23963
Laursen B, Hafen CA, Kerr M, Stattin H. Friend influence over adolescent problem behaviors as a function of relative peer acceptance: to be liked is to be emulated. Journal of abnormal psychology. 2012;121:88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024707
Assanangkornchai S, Mukthong A, Intanont T. Prevalence and patterns of alcohol consumption and health‐risk behaviors among high school students in Thailand. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2009;33:2037-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01043.x
Weinberger AH, Sofuoglu M. The impact of cigarette smoking on stimulant addiction. The American journal of drug and alcohol abuse. 2009;35:12-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00952990802326280
Ren M, Lotfipour S. Nicotine Gateway Effects on Adolescent Substance Use. The western journal of emergency medicine. 2019;20:696-709. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5811/westjem.2019.7.41661
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The Journal of Southeast Asian Medical Research will hold the copyright to all published articles. The publisher's production department handles copyright forms once a manuscript is accepted and scheduled for publication.







